Introduction
In SQL Server, Virtual Log Files (VLFs) are smaller segments within a physical transaction log file. They are used to manage and organize the transaction log efficiently. Here’s a concise overview:
Key Points about VLFs:
- Structure:
- Each physical transaction log file is divided into multiple VLFs.
- The number and size of VLFs are determined dynamically when the log file is created or extended.
- Purpose:
- VLFs help SQL Server manage log space efficiently by allowing portions of the log to be reused or truncated as needed.
- Performance Impact:
- Having too many VLFs (due to frequent small log file growths) can degrade performance, especially during recovery or log backups.
- Conversely, very large VLFs can delay log truncation and impact performance.
- Best Practices:
- Pre-size transaction log files to avoid frequent auto-growth.
- Use a reasonable growth increment (e.g., 512 MB or 1 GB) to prevent excessive VLF creation.
- Monitoring:
- You can monitor VLFs using the
DBCC LOGINFOcommand or tools like SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
- You can monitor VLFs using the
By effectively managing VLFs, you can optimize SQL Server’s performance and ensure smooth transaction log operations.
2. Configuration
All databases receive a VLF reduction (VLF > 1000)
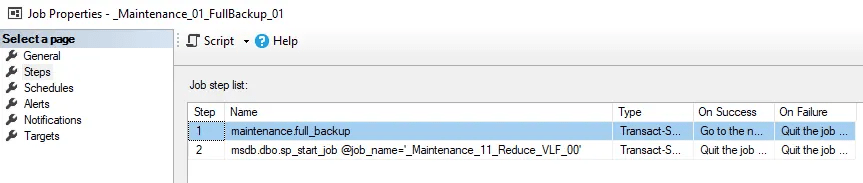
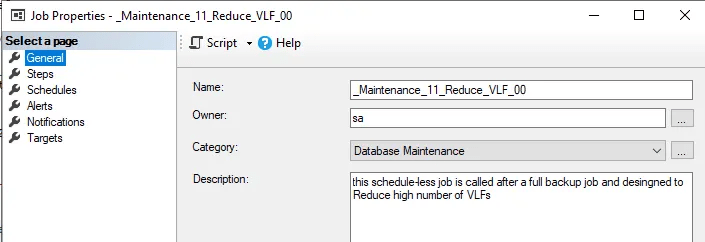
Regular Schedule: After full backup job of Every Saturday at 10:30PM